Antibe, France, December 23, 2022
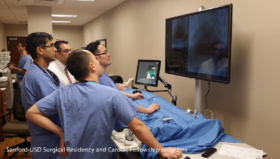
The EACVI and Surgical Science have joined forces to create a unique TOE online simulator, aiming to evaluate TOE knowledge and performance level among young cardiologists and assess the need for simulation training for this purpose.
The study, which included over 716 cardiologists from 81 countries tested online, revealed that there is a TOE skill deficiency among young cardiologists and emphasized the increasing need for TOE simulation-based training.

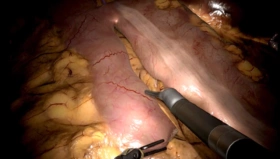
Transesophageal echocardiography (TOE), an important cardiovascular imaging modality, is considered safe when properly conducted, but can cause complications, even in the hands of experienced practitioners. Therefore, establishing basic competencies in a controlled, simulation setting is an opportunity to reduce procedural risk.
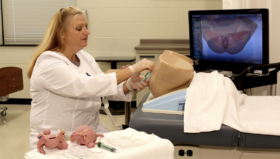
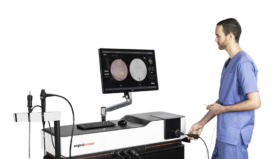
A study has shown that Simbionix Ultrasound Mentor simulator for TOE training is effective and may reduce the number of real patient TOEs required for training purposes¹.
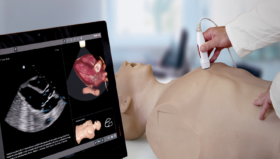
The COVID-19 pandemic has required medical educators to adapt their teaching approach to remote, thus leading Surgical Science to initiate a pioneering project of ultrasound cloud-based simulation, in which trainees can navigate a virtual TOE probe to capture standard views and train remotely from anywhere, at any time.
In collaboration with EACVI Heart Imagers of Tomorrow (HIT) committee, an assessment for TOE skills and knowledge was developed, in which the trainee follows the scan protocol to capture 10 standard views and identify anatomical structures in each.
Online TOE Simulator Study
716 young cardiologists from 81 countries participated in the study and completed two tests: TOE knowledge test and a practical test using an online TOE simulator to evaluate skills².
Dr. Theo Pezel, French ambassador of HIT EACVI: “This collaboration was a pioneering pilot in remote training and assessment of TOE knowledge and skills. Based on the largest international online study assessing theoretical knowledge and practical skills in TOE among young cardiologists around the world, we emphasized a relatively low level of TOE skills and knowledge, with a growing need for simulation-based training.”
The study also found that prior participation in a TOE simulation-based training session, a higher number of TOE exams performed per week, and the EACVI certification for TOE were independently associated with a higher global score. These findings emphasize the important impact of EACVI certification regarding TOE knowledge and skills for all young cardiologists.
In accordance with the EACVI recommendations for training, competence, and quality improvement in echocardiography² simulation-based training programs are the present and the future of TOE teaching. The relevance and implementation of this kind of program is currently being tested by the ongoing randomized SIMULATOR study³.
Surgical Science continues to invest in developing new simulation technologies, including cloud-based simulation, in order to enable training in distant locations to a wide audience with no limits.
https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(16)36356-5/fulltext
https://academic.oup.com/ehjcimaging/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ehjci/jeac195/6712774
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2021.661355/full=